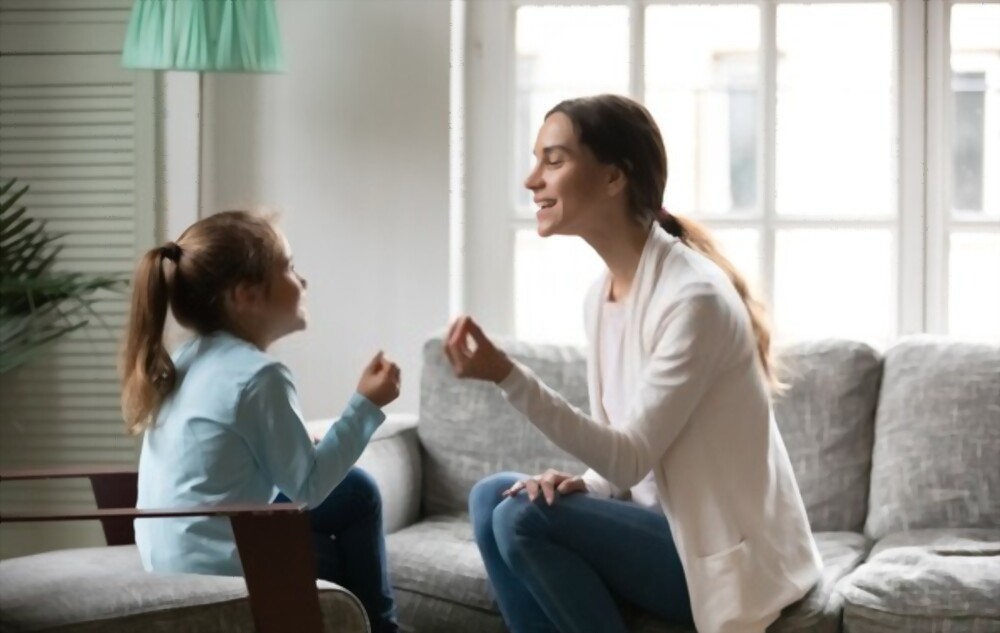
Dyspraxia, also known as developmental coordination disorder (DCD), is a learning difficulty that affects an individual’s fine and gross motor skills, speech, and coordination. It can significantly impact a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks and motor activities. From simple actions to more complex tasks, dyspraxia poses significant challenges and requires compassionate support. However, with person-centred care and a deep understanding of the challenges individuals with dyspraxia face, people can learn effective strategies and lead independent and fulfilling lives.
What is Dyspraxia?
Dyspraxia is a learning difficulty that impacts an individual’s motor skills and coordination abilities. It usually manifests in childhood and persists into adulthood. People with dyspraxia may also experience challenges with language, thought processing, and perception.
The root cause of dyspraxia lies in the brain processing and transmitting neural messages that govern motor functions. However, it is crucial to recognise that dyspraxia does not affect a person’s cognitive capacity, even though it may lead to learning and developmental delays.
The diagnosis is typically carried out by healthcare professionals who assess the individual’s motor skills and coordination difficulties. Early identification and intervention of dyspraxia are crucial in managing symptoms and enhancing motor skills and coordination. Treatment approaches may involve occupational therapy, physical therapy, and other specialised interventions tailored to the individual’s needs.
With proactive support, individuals with dyspraxia can overcome challenges and reach their full potential, highlighting the importance of raising awareness and understanding to foster inclusivity.
Dyspraxia in Adults
Signs of dyspraxia are noticeable from a young age, but this learning difficulty may go unrecognised until adulthood. Males are more likely to be affected by dyspraxia than females. However, the identification of dyspraxia in females more commonly happens when they are older, as opposed to in childhood.
Adults may experience difficulties in executive functioning, organisation, and memory. It’s important for individuals to have accommodations in their work environment, and many people can benefit from assistive technologies and support planning.
Healthcare providers may also use the term dyspraxia to describe movement difficulties later in life, which can be the result of brain injuries or stroke, known as acquired dyspraxia.
Dyspraxia in Children
Dyspraxia is often diagnosed in childhood and many children show signs of developmental delay in motor skills and language.
Dyspraxia affects a child’s coordination skills, making activities like riding a bicycle or playing sports difficult. It also affects a child’s fine motor skills, which can cause challenges with writing or fastening buttons. While children with dyspraxia may face challenges, their intellectual ability is not affected.
Identifying dyspraxia at an early age is crucial. Tailored support services can help children reach their potential and development in this area.
Types of Dyspraxia
There are different types of dyspraxia:
- Motor Dyspraxia – challenges with writing, dressing, or walking. It creates difficulties in performing a sequence of movements, like brushing teeth, making a bed, combing hair or waving a hand
- Verbal Dyspraxia – challenges with speech and language
- Oral Dyspraxia – challenges with mouth and tongue movements. It may create difficulties with eating and swallowing
Identifying the specific type of dyspraxia a person has is crucial in creating a personalised care plan that can help enhance their abilities. Every individual is different, and early recognition of their symptoms can make a significant difference in their journey towards overcoming dyspraxia.
Signs and Symptoms of Dyspraxia
Every person is unique, and dyspraxia can affect individuals differently and with varying degrees of severity. Mild symptoms may be experienced by some, while others may face more challenging obstacles that can impact their daily lives, including education and work.
Common signs and symptoms of dyspraxia include:
Challenges with fine motor skills and tasks that require precise hand-eye coordination, such as tying shoelaces, buttoning shirts, using utensils, or manipulating small objects.
Challenges with gross motor skills, making activities like running, jumping, hopping, or balancing. People that have dyspraxia may appear clumsy or uncoordinated in their movements.
Difficulty with spatial awareness and perception. Individuals may have difficulty judging distances, spatial relationships, and coordinating their movements within physical spaces.
Challenges with organisation and planning. Individuals may need help with tasks that require sequencing, prioritising, and managing time effectively.
Challenges with speech and language, such as articulation, pronunciation, word retrieval, and expressing verbally.
Challenges with sensory processing. Individuals may be sensitive to sensory input, such as touch, sound, taste, or smell, impacting their ability to filter and process sensory information effectively.
Proper assessment and diagnosis by a healthcare professional are essential for identifying and understanding the specific challenges faced by individuals.
Symptoms of Dyspraxia in Adults
Adults with dyspraxia often avoid social situations and may face challenges at school or the workplace. However, with proper support, adults with dyspraxia can live a fulfilled life.
Symptoms of dyspraxia in adults include:
- Difficulty completing chores
- Difficulty with writing and drawing
- Difficulty coordinating both sides of the body
- Unclear speech
- Challenges with grooming, dressing, or applying makeup
- Difficulty planning and organising thoughts and tasks
- Difficulty sleeping
- Difficulty distinguishing sounds from background noise
- Lack of rhythm when dancing or exercising
- Difficulty learning new motor skills
- Difficulty applying skills in a different or busy environment
- Difficulty handling tools and equipment such as a tin opener
- Challenges with balance
- Difficulty with time management skills
A person-centred support plan tailored to an individual’s unique needs is crucial in providing proactive support.
Symptoms of Dyspraxia in Children
It’s important to know that dyspraxia affects each child differently, and not all children with dyspraxia will display the same symptoms.
Symptoms of dyspraxia in children include:
- Delay in acquiring early motor skills such as sitting, crawling, walking
- Movement difficulties like running, jumping, or hopping
- Slow and hesitant movements
- Slow writing
- Difficulty getting dressed
- Works better alone or in a small group
- Difficulty following instructions
- Difficulty using scissors, colouring and drawing
- Difficulty processing thoughts
- Difficulties with concentration
- A higher tendency to bump into things, to fall over, and to drop things
- Difficulty learning new skills
Encouragement, practice, and a customised care plan are proactive methods to help children overcome their challenges and gain confidence in their unique abilities.
Causes of Dyspraxia
The precise cause of dyspraxia remains uncertain. Nonetheless, research suggests a connection to the development of motor neurons, which are responsible for controlling muscles. Dyspraxia is part of neurodiversity and a neurotype.
Besides this, other potential factors have been associated with dyspraxia, such as genetic components, premature birth, and low birth weight.
It’s important to recognise that dyspraxia is complex and likely influenced by a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. In-depth research is necessary to gain a deeper understanding of the causes and mechanisms driving dyspraxia, which will ultimately contribute to more effective treatments and support strategies.
Dyspraxia Assessment
Dyspraxia is typically diagnosed during childhood when children exhibit difficulties with their motor movements. A multidisciplinary team of professionals collaborate to assess the child’s coordination, balance, and motor skills. This comprehensive evaluation involves observing the child’s abilities and comparing them to developmental milestones during various everyday activities.
Similarly, the diagnostic process for adults follows a similar path, where a team of medical professionals assesses an individual’s balance, coordination, and motor skills.
By conducting thorough assessments, these professionals can accurately identify dyspraxia in both children and adults, allowing for timely and appropriate intervention strategies. Early diagnosis is essential as it enables individuals with dyspraxia to receive the necessary support and targeted therapies, enhancing their overall quality of life and maximising their potential for personal growth and independence.
Treatments for Dyspraxia
Dyspraxia is a lifelong learning difficulty. However, with the appropriate therapy, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and enhance their skills and abilities. It is important to recognise that treatment for dyspraxia is highly individualised, tailored to meet the unique needs of each person. As individuals progress in their therapy journey, treatment plans may be adjusted and fine-tuned to ensure the most effective outcomes.
Healthcare providers collaborate closely with multidisciplinary teams to provide comprehensive support. Behaviour analysts play a crucial role in helping individuals improve social skills, self-help skills, and communication abilities. Paediatric specialists contribute their expertise in addressing both medical and psychosocial aspects of a child’s development, offering a holistic approach to care. Additionally, psychologists offer valuable assistance in managing stress, developing coping skills, and addressing mental health concerns.
Through this collaborative approach, individuals with dyspraxia receive personalised and comprehensive care, enabling them to thrive and reach their full potential.
Perceptual Motor Training
Perceptual motor training is vital for improving language, visual, movement, and auditory skills. The training includes a series of tasks that gradually become more advanced. Perceptual motor training can be tailored to the specific needs and abilities of individuals, considering their age, developmental stage, and areas of difficulty. It is typically conducted under the guidance of professionals specialising in sensory and motor development.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy helps a person to develop and learn new skills for daily activities that otherwise are difficult for people with dyspraxia. The therapy involves observation at work or school and reaching specific goals regarding performing various everyday tasks and activities.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy helps people with dyspraxia improve their motor skills with movement and exercise. Physical therapy involves a combination of therapeutic techniques, exercises, and educational strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. The primary objectives of physical therapy are to enhance motor skills, optimise physical functioning, and promote independence in daily activities. Also, a skilled physical therapist can work closely with individuals with dyspraxia to assess their unique challenges and develop a personalised treatment plan.
Speech and Language Therapy
Speech and language therapy helps people communicate more effectively. The treatment plan involves exercises to overcome difficulties when making certain sounds. A skilled speech-language pathologist (SLP) collaborates closely with individuals with dyspraxia to develop a tailored treatment plan that aligns with their unique needs and goals.
Additionally, speech and language therapy is often conducted in a one-on-one setting, although group therapy sessions can also be beneficial for practising communication skills. It provides strategies, resources, and recommendations to support individuals with dyspraxia in various environments, such as home, school, or work settings.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that can be beneficial for dyspraxia. It is a collaborative approach that addresses the connection between thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. While CBT is often referred to as talk therapy, it goes beyond just talking and aims to facilitate positive changes in thinking patterns and behaviour characteristics, improving confidence and self-esteem.
Dyspraxia Related Conditions
In many instances, a child or adult with dyspraxia may have other conditions or challenges with overlapping symptoms.
Some of the related conditions and challenges included:
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Apraxia
- Dyscalculia
- Dyslexia
Other difficulties, such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, can cause physical symptoms like dyspraxia. It’s essential to get an accurate diagnosis to determine the most effective therapy strategy.
Below, we explain some of the challenges related to dyspraxia.
Dyspraxia and Dyslexia
According to findings, about 51% of children diagnosed with dyslexia also have dyspraxia. There is an overlap between the symptoms, such as challenges with writing and language. However, dyslexia is primarily a learning difficulty related to reading, writing, and spelling, while dyspraxia is a difficulty in motor coordination skills.
Dyspraxia and Autism
Many studies show an overlap between the symptoms of dyspraxia and Autism, such as difficulties with spoken language, difficulty with planning, and problems concentrating. Like dyspraxia, Autism is part of neurodiversity, and it affects socialisation and communication, while dyspraxia affects motor skills and physical coordination.
Dyspraxia and ADHD
ADHD is a learning difficulty that impacts attention, behaviour, and hyperactivity. Symptoms of ADHD can overlap with dyspraxia, including challenges with handwriting and difficulties planning tasks. By being aware of the symptoms and implementing personalised support plans, healthcare professionals can help people with dyspraxia and ADHD overcome their unique challenges.
Living with Dyspraxia
Individuals with dyspraxia can lead fulfilling lives when provided with the right diagnosis and support. Personalised treatment approaches, such as occupational therapy and speech therapy can effectively improve symptoms and enhance overall functioning. Furthermore, there are various tools and strategies available to help individuals overcome challenges associated with dyspraxia.
Some helpful recommendations for managing dyspraxia include engaging in regular exercises and physical activities to enhance muscle strength, including practising sports to improve coordination. Utilising planners, calendars, and alarms can aid in organising projects, assignments, or daily tasks. Additionally, breaking larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps can make them more approachable, and seeking professional assistance for more complex tasks can provide valuable support.
How Does LD Network Support Individuals with Dyspraxia?
At LD Network, we specialise in designing personalised plans specifically tailored to address the unique challenges of dyspraxia, ensuring that individuals receive the precise support they need to thrive in their daily lives.
We have extensive experience working with multidisciplinary teams, and our clinicians are highly trained to effectively provide comprehensive care and support. LD Network supports people with learning difficulties, learning disabilities and complex care needs to live whole and meaningful lives.
To learn more about our person-centred care, contact us today, or visit our office in Exeter.