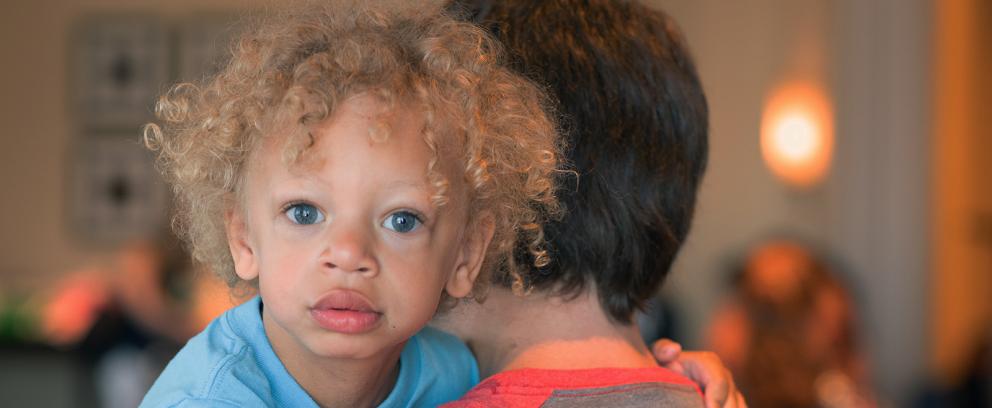
Williams syndrome is a neurodevelopmental difference in people that appears due to a random genetic mutation. Children and adults with Williams syndrome have a unique, endearing personalities, distinctive physical features and specific learning differences. Learn more about the symptoms and causes of WS and how our humanised approach can empower the individual to live an independent and rewarding life.
What is Williams Syndrome?
Williams syndrome, also known as Williams-Beuren syndrome, is a genetic variation present at birth. The syndrome appears due to a deletion of specific genes in chromosome 7. Williams syndrome typically occurs with particular medical challenges, such as mild to moderate learning difficulties, developmental delays, and distinctive physical traits.
The physical and neurodevelopmental differences often go hand in hand with outstanding verbal skills, highly outgoing personalities and an incredible affinity to music. Having a person with WS around you can foster positive energy, empathy and heart-warming hospitality. The following lines will reveal the multiple-facet approach to Williams syndrome.
How Common is Williams Syndrome?
Williams syndrome occurs in 1 in approximately 10,000 people. The genetic variation appears with a random deletion of the 26-28 genes on chromosome 7 during conception. According to the Williams syndrome association, WS can equally appear in both males and females in all populations around the globe.
People with Williams syndrome have not inherited the genetic mutation from their parents. Experts suggest that people with Williams syndrome are 50% likely to pass the altered genetic material to their children.
Why Is Williams Syndrome Called the Happy Syndrome?
Williams syndrome is also called “The Happy Syndrome” or “The Beautiful Mystery” as people with WS tend to be very social, friendly and radiating positive energy. They have a unique sense of empathy, kindness and a high emotional connection to music.
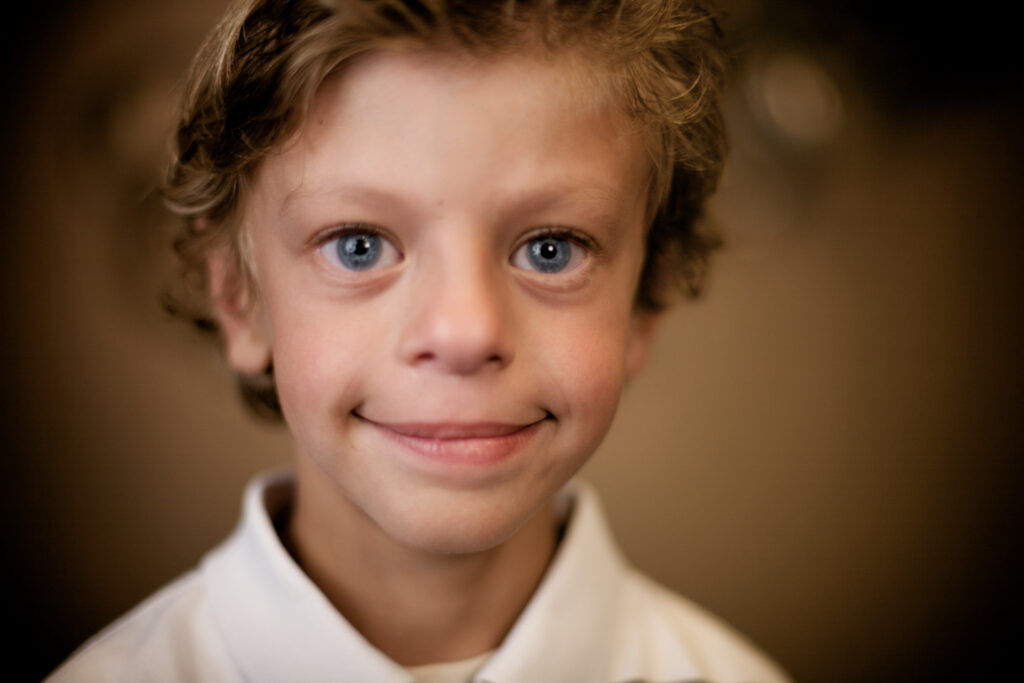
Williams Syndrome Symptoms
The absence of the specified genetic material is associated with the distinctive physical characteristics and health challenges of people with Williams syndrome. Common symptoms of WS involve characteristic facial features, medical difficulties and mild to moderate delay in cognitive development.
Facial Features
Adults and children with Williams syndrome often have distinctive facial features, including:
- Wider forehead
- Flattened bridge on the nose
- Wider mouth
- Small chin
- Puffed cheeks
- Elongated face (in adults)
- Smaller teeth with a broader space between

Musculoskeletal Symptoms
Williams syndrome affects the musculoskeletal health and development of individuals. For example, children with Williams syndrome might have joint hypermobility (hyper extensive joints), whilst adults may experience joint stiffness contracture. Other possible musculoskeletal symptoms of Williams syndrome include:
- Kyphosis
- Lordosis
- Scoliosis
- Radioulnar synostosis
- Gait difficulties
Musculoskeletal deviations are a common health challenge for many people, including children and adults. Early intervention and physical therapy can result in promising outcomes and significant improvement.
Physical Characteristics
Sometimes people with Williams syndrome experience different health challenges that might seek attention and proper assessment. Adults and children with Williams syndrome might face the following:
- Feeding difficulties
- Low birth weight
- Increased blood calcium levels (hypercalcemia in children)
- Heart and blood vessels difficulties
- Specifically supravalvular aortic stenosis
- High blood pressure
- Trouble eating
- Chest pain
- Vertical skin folds
- Hypersensitivity to sound
- Early puberty
- Kidney and urinary tract infections
Physical characteristics and related medical difficulties are different in each person. Therefore, early evaluation and proper care are paramount for people with Williams syndrome to live independent and fulfilling lives.
Psychological Symptoms
Adults and children with Williams syndrome have distinctive personality characteristics as well. For example, they tend to be very engaging in social interactions, friendly and emphatic with others, even those who don’t show sympathy towards them.
People with Williams-Beuren syndrome are exceptionally kind and vibrant, with a unique fondness for music. Recent research showed that the reason behind this sociability is associated with the size of the amygdala, a brain structure responsible for emotions, behaviour and cognitive abilities. Specifically, the amygdala in people with Williams syndrome seems to be larger than the rest.
The larger amygdala in people with WS is associated with increased:
- emotional sensitivity
- sociability
- anxiety
- emotional distress
- attention deficit disorder
- fear of strong and sudden sounds
Developmental Delays
The chromosome mutation in Williams syndrome may result in various cognitive difficulties and developmental disabilities such as delayed speech and walking and acquiring new skills compared to children of the same age. Learning difficulties might also be present, accompanied by attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
At the same time, children with Williams syndrome have strong memory skills and the ability to learn new things quickly. They have good speaking and reading powers and a great talent for music.
What Causes Williams Syndrome?
Williams syndrome is caused by a lack of a specific section in the genetic material on chromosome 7. This missing genetic information is associated with characteristic facial features, physical differences and behavioural variations.
In most cases, Williams syndrome occurs naturally during the formation of the egg cell or sperm of parents who are not WS carriers. However, it can also be inherited, although rarely, from a parent who has the WS. This is known as autosomal dominant inheritance, meaning that only one copy of the altered gene can cause genetic variation. For example, when a child has a parent with a mutated gene, it has a 50% chance of inheriting the modified gene.
The genetic variation in people with Williams-Beuren syndrome includes a lack of an essential protein in the body known as elastin. This protein provides elasticity and flexibility to different body structures such as skin, joints, heart and blood vessels. The absence of elastin is associated with the distinctive physical characteristics and health challenges of people with Williams syndrome.
How is Williams Syndrome Diagnosed?
Williams syndrome can be diagnosed when your child is a baby or until four. Typically, your physician may notice the distinctive facial features and request further examination.
If a physician suspects your child might have Williams syndrome, they will probably provide a genetic blood test and physical examination.
Standard DNA blood tests for WS include:
- FISH ( Fluorescence In Situ Hybridisation) test
- Microarray analysis test
Also, your healthcare provider might perform an EKG (electrocardiogram) in addition to a heart and kidney ultrasound.
Other Conditions Related with Williams Syndrome
The genetic influences of Williams syndrome are related to variations in neural mechanisms that can further lead to potential health difficulties. More precisely, the lack of genetic material in WS can potentially lead to heart and blood vessel difficulties and problems with the gastrointestinal and urinary tract.
Common health conditions related to Williams syndrome include:
- Aortic stenosis – narrowing of the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body
- Narrowed arteries in the lungs
- Hypertension- increased blood pressure
- Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
- Weight gain and diabetes ( in adults)
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Hearing and vision difficulties
Difference Between Williams Syndrome and Down Syndrome
Williams syndrome and Down syndrome result from genetic variations affecting different segments of the DNA in people. More precisely, genetic modifications in people with WS and Down syndrome are distinctive and affect different parts of the chromosome structures.
Typically, people with Williams syndrome come with visuospatial challenges but have good language skills and social personality. On the other hand, children with Down’s syndrome have good visuospatial skills but might face language and social challenges.
Treatment for Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome is a lifelong variation. Although it has no cure, early intervention and bespoke care allow people with WS to live a quality and meaningful life. Most healthcare providers recommend a well-rounded approach towards identifying and managing the specific health challenges of people with Williams syndrome.
The most common pathway towards handling WS symptoms includes:
- Cardiovascular therapy and regular medication (if needed)
- Gastrointestinal and endocrine therapy (if needed)
- Speech and language therapy
- Behavioural therapy
- Physical therapy
- Vision or hearing therapy (if needed)
Family education and genetic counselling are also important for parents to understand and learn how to help their children cope with their differences and everyday challenges. By embracing their diversity, people and the community can appreciate their positivity, talents, and, and love for life.
How LD Network Supports Individuals with Williams Syndrome
At LD Network, our way of supporting people with learning disabilities and other complex care needs is a little different. We provide a multi-component approach, always putting people at our story’s centre.
We provide humanised care in stages, specifically tailored to the needs of the individual. Our PBS framework ensures that every individual is treated with dignity and respect. We celebrate diversity and leverage people’s skills, talents and powers. Our goal is to help every individual live an independent and rewarding life.
Contact us for further information.