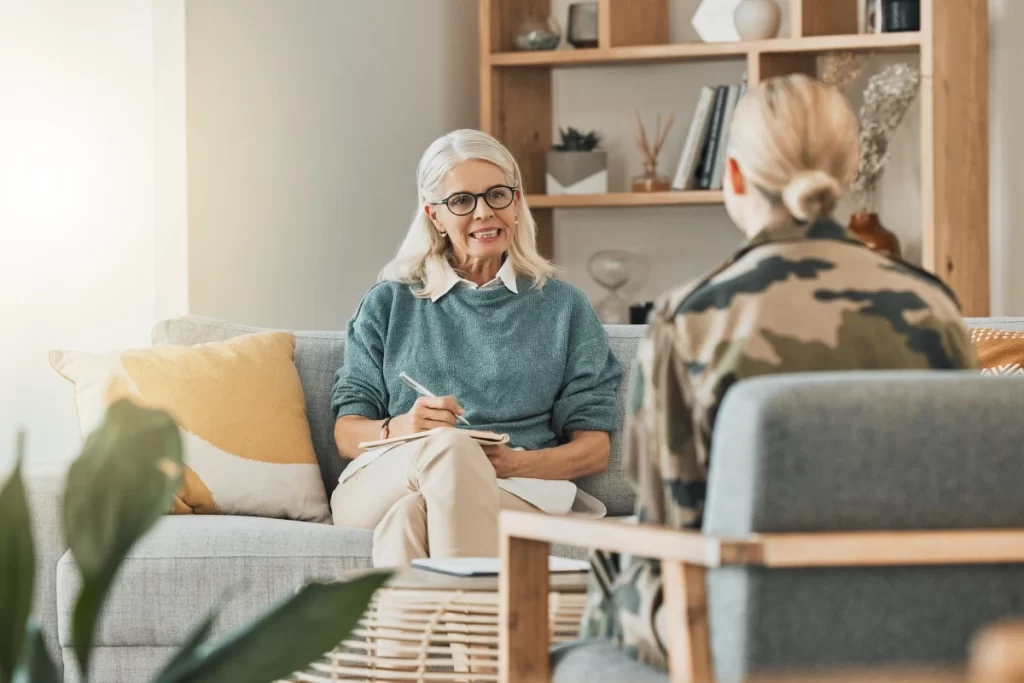
While healthcare organisations recognise the crucial role of compliance, they must ensure that quality of care remains at the forefront of care delivery. This post explores the relationship between healthcare compliance and quality of care, providing insights to help providers balance these vital elements. It also outlines essential strategies for advancing compliant operations while ensuring excellence in care delivery, aiming for humanised care and positive outcomes.
The Link Between Compliance and Quality of Care in the Healthcare Industry
Healthcare organisations navigate a complex compliance law that stretches across diverse sectors, encompassing entities from pharmacies and insurance companies to cloud service providers. Healthcare compliance demands an ongoing commitment to follow legal, ethical, and professional standards inherent to healthcare practices.
A compliance program serves as more than a mere rule-following mechanism. It becomes a driving force for continuous improvement, addressing aspects ranging from the privacy of individuals to overall operational improvement. The risk of not following compliance obligations includes regulatory penalties and jeopardises the foundational commitment to quality of care. This emphasises the link between compliance and the very essence of healthcare itself.
The scope of compliance is extensive, covering both internal and external practices, with the primary aim of ensuring comprehensive understanding and following correct procedures throughout the organisation. While compliance is a crucial effort tied to periodic accreditations, quality of care is a continuous journey. Recognising the critical link between compliance and quality of care involves understanding that compliance establishes the baseline, and quality of care improvement becomes the pathway to optimal outcomes for individuals in healthcare settings.
The Importance of Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a vital aspect of healthcare operations, including processes and procedures that ensure an organisation’s follows laws, industry regulations, and contractual obligations. A strong compliance program is mandatory in highly regulated and high-risk healthcare environments, forming the foundation for effective operation. The stakes are exceptionally high in healthcare, where noncompliance can have severe consequences, potentially affecting individual outcomes, care coordination, and safety.
Every individual within a healthcare organisation plays a role in maintaining compliance. Implementing healthcare compliance initiatives brings a multitude of benefits. Compliance safeguards against legal risks, fosters improved care, and levels the playing field in competitive healthcare. Regulatory compliance in healthcare involves navigating complex laws designed to protect privacy and ensure quality of care and laws aimed at safeguarding healthcare workers. Compliance is an ongoing commitment that protects the organisation from legal pitfalls and is a cornerstone for building a reputation as a trusted and respected healthcare provider.
Quality of Care in Healthcare
Quality of care in healthcare ensures that individuals receive person-centred care and effective treatment. It involves providing safe, timely, person-centred, efficient, and equitable healthcare services. Quality of care leads to improved individual outcomes, satisfaction, and overall healthcare system performance. Healthcare providers deliver humanised care by following evidence-based practices, promoting communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, and prioritising individuals’ preferences. Continuous quality improvement initiatives, monitoring and evaluation systems, and technology integration further improve the standard of care.
The Challenge of Balancing Compliance and Quality
The healthcare industry faces a complex challenge in balancing regulatory compliance with the delivery of high-quality care. One of the primary obstacles is the dynamic nature of healthcare regulations, which frequently change. Staying abreast of these updates demands considerable time and effort from healthcare providers. Compliance management needs an efficient approach to ensure healthcare organisations meet current standards and are well-prepared for upcoming changes.
The prevalence of data breaches poses another significant challenge, especially in the digital age. Protecting individuals’ data remains a paramount concern, requiring robust cybersecurity measures. The collection, storage, and management of individuals’ information make healthcare organisations attractive targets for cyber threats, demanding the implementation of updated security systems and regular cybersecurity training for staff.
The start of telemedicine, accelerated by the pandemic, further complicates compliance efforts. Regulating this new approach to care delivery requires careful consideration, especially concerning the intersection of telehealth and cybersecurity regulations. Lastly, acquiring and retaining talent within the healthcare sector is an ongoing challenge. The need for an in-depth yet ethically compliant screening process becomes crucial to identify and keep expert healthcare professionals, ensuring the seamless implementation of policies aligned with regulatory standards. Balancing compliance and quality in healthcare necessitates a strategic, adaptive, and comprehensive approach to overcome these challenges.
The Consequences of Non-compliance
Non-compliance carries severe consequences, impacting financial stability, operational continuity, and overall reputation. Failing to follow regulatory standards can result in fines, penalties, and other fees. These financial repercussions can pose a significant threat to the economy of healthcare organisations. However, the consequences of non-compliance extend beyond financial impacts and limit investments in necessary equipment and services, potentially compromising the quality of care.
Here is a list of consequences associated with non-compliance in the healthcare industry:
- Reputation damage – Loss of trust and confidence can have long-lasting effects on an organisation’s ability to attract new talent and retain existing talent.
- Loss of revenue – This can impact the organisation’s financial stability and limit investments in necessary medical equipment and services.
- Loss in productivity – Fewer individuals can be supported, affecting the organisation’s ability to treat the same number of individuals effectively.
- Assets confiscation – In extreme cases, non-compliance may lead to the confiscation of assets, adding to the financial losses incurred by the organisation.
- Loss of Trust – Individuals may lose trust in healthcare providers who fail to safeguard sensitive information, potentially seeking alternative healthcare options.

Strategies for Balancing Compliance and Quality
A strategic approach is imperative to balance regulatory compliance with delivering high-quality care. For this, healthcare workers must comprehend how systems and processes can harmonise with personalised care.
Establishing a healthcare compliance plan involves:
- Appointing a compliance officer and a dedicated team.
- Implementing robust employee education and training programs.
- Fostering effective communication channels for reporting concerns.
- Having well-defined processes to respond to complaints and violations.
In the following sections, we will provide a detailed explanation of these strategies and some additional ones.
Training and Education Programs
Training and education should be an ongoing and comprehensive process rather than a one-time initiative. Employee training is fundamental, involving the entire team in learning best practices, fraud prevention strategies, and service delivery aligned with the organisation’s values. Healthcare organisations must implement regular training sessions, workshops, and updates to inform staff about the latest compliance requirements and best practices. This includes healthcare professionals, administrative staff and support staff.
Regular Audits and Quality Assessments
Monitoring and audits are integral components of maintaining compliance within the healthcare industry. In addition to monitoring, risk mapping is essential to assess and understand all the risks a healthcare institution is exposed to, particularly concerning data protection laws to ensure data privacy. Once risks are identified, mitigation strategies should be implemented, which may involve process improvements, policy revisions, or additional training. Proper documentation of these policies is essential for demonstrating compliance efforts and providing a reference for team members. Internal audits by a dedicated compliance team identify areas for improvement, reinforcing the company’s commitment to compliance and updating policies and procedures based on audit findings to better prepare for regulatory scrutiny.
Engaging in Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
Engaging in Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) within the healthcare sector is a dynamic and ongoing process to improve care and overall efficiency. CQI establishes a framework that fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
This systematic approach involves a cycle of analysing healthcare processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes. Subsequently, it includes monitoring outcomes and adjusting strategies based on the results obtained. The central view of CQI is a relentless pursuit of better healthcare by consistently questioning how current practices can be refined and optimised.
The overarching goals of CQI include many aspects. These include cost reduction, decreased appointment and in-department wait times, reduced cycle time, and defect reduction. Critically, it also improves individual and staff safety and overall satisfaction.
Person-centred Approach
A person-centred approach emphasises the individuality and unique needs of each individual. This approach places the individual at the heart of decision-making processes, fostering a collaborative partnership between healthcare providers and individuals. It involves open communication, shared decision-making, and tailoring healthcare plans to align with the individual’s goals and preferences. This approach improves overall satisfaction and contributes to improved health outcomes by promoting active engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
A person-centred approach becomes increasingly relevant in the context of compliance and quality of care. It emphasises the critical importance of tailoring compliance strategies to individual care plans. Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure ongoing safety of individuals. Central to this process is the accessibility of evaluation reports, which is vital for accurate monitoring and reporting. Establishing a robust system that provides easy access to this information is crucial for highly personalised care and support services. By addressing safety concerns through a person-centred lens, healthcare organisations uphold individuals’ safety and improve their reputation as responsible and person-centric providers.
Open Communication and Collaboration
Open communication and collaboration stand out as fundamental pillars for success between compliance and quality of care in healthcare. This requires a culture that encourages transparent and open communication channels across all healthcare organisation levels. Also, there is a need for an environment where team members feel empowered to express concerns, share insights, and contribute to the continuous improvement of processes. Clear and effective communication is paramount in conveying compliance requirements and quality standards, ensuring that all staff members are well-informed and aligned with organisational goals. By breaking down silos and encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration, healthcare organisations can leverage diverse expertise to manage complex compliance frameworks while concurrently improving the quality-of-care delivery. Open lines of communication foster a collaborative spirit where teams collectively address challenges, share best practices, and work towards harmonising compliance measures with quality of care.
LD Network Balances Compliance and Quality of Care
LD Network adopts a proactive approach to achieving a balance between compliance and quality of care. Our commitment is based on a comprehensive understanding of regulatory frameworks, ensuring that we align with established standards while concentrating on optimising the quality of care we provide to our community.
Recognising the importance of seamlessly integrating compliance measures and quality improvement initiatives, we partner with healthcare organisations to create a healthcare environment prioritising individual safety, efficiency, and positive outcomes.
Within LD Network, our dedicated clinicians collaborate across disciplines to follow compliance requirements while providing person-centred and humanised care. We have developed a training program designed to equip clinicians with the knowledge required to follow processes, procedures, and standards, ensuring consistent care delivery across diverse healthcare settings.
If you are a healthcare provider in search of staffing solutions that prioritise compliance and quality of care, contact our office in Exeter to discover how we can help you.
Contact us today.